A quick explanation of mycorrhiza fungi and its importance
The importance of maintaining good soil conditions to promote and assist your plants in teaming up in a symbiotic relationship with mycorrhiza fungi
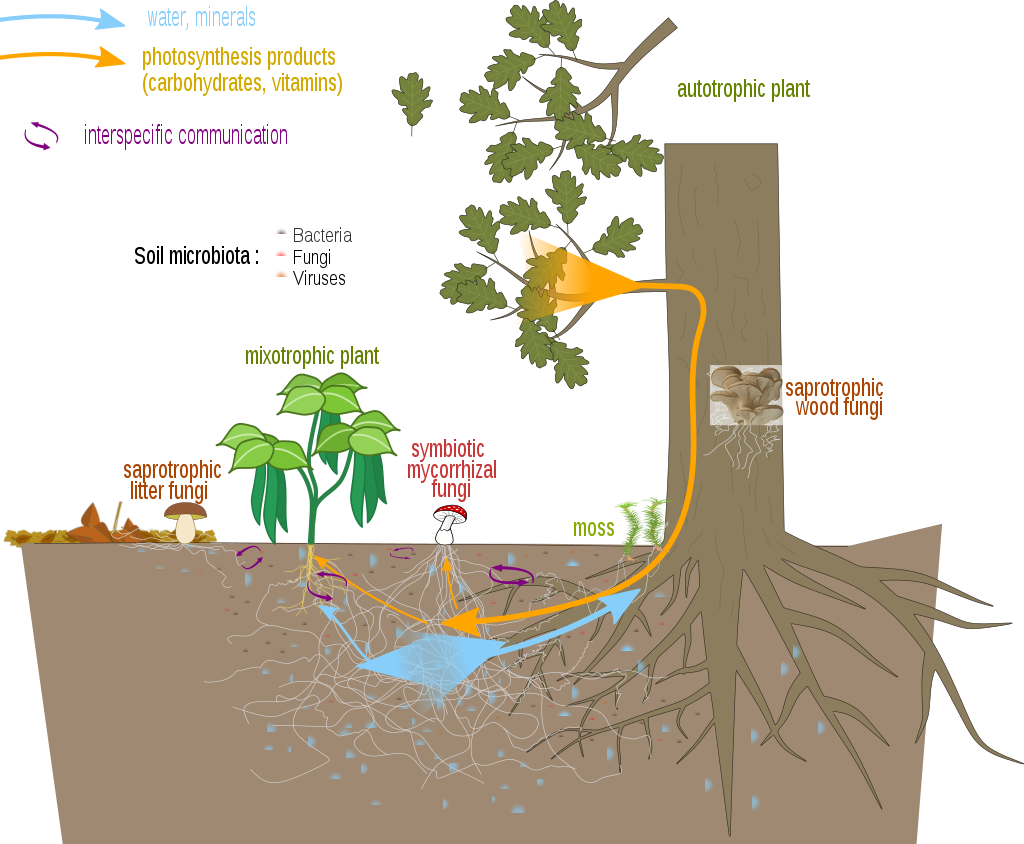
Within mutualistic mycorrhiza, the plant gives carbohydrates (products of photosynthesis) to the fungus, while the fungus gives the plant water and minerals in exchange.
Mycorrhizal fungi are in a symbiotic relationship with plants. The relationship is usually mutualistic, the fungus providing the plant with water and minerals from the soil and the plants providing the fungus with photosynthesis products. Some fungi are however parasitic, taking products from the plant without providing benefits. Conversely, some mixotrophic or parasitic plants connect with mycorrhizal fungi as a way to obtain photosynthesis products from other plants. Finally, saprotrophic (or saprophytic) fungi live on dead organic matter without establishing a symbiosis with plants.
The importance of mycorrhiza fungi in relation to climate change is that maintaining and creating idea conditions for mycorrhiza and your plants especially trees dramatically improves the rate at which plants can remove carbon from atmosphere and soil helping to reduce the effects of global warming and improve local climates.